Sugarcane red rot control
(1) Disease and Incidence
1 Main diseases: Red rot mainly damages the stems and midribs of the cane, and leaf and leaf sheaths occur occasionally. The pathogens are invaded by stem cuttings and plant wounds. The injured cane stem has no symptoms in the early stage, but the sugarcane stem shows reddish or dark red color in the longitudinal section of the cane, and has a sour taste. After that, the cane stem tissue turns brown and red, and the outer surface of the decayed stem appears dark red patches, and the victim's depression dies. The middle veins of the leaves are damaged. The lesions appear as red dots at the beginning of the lesion. They spread into a spindle or strip shape along the midrib. Afterwards, the center becomes pale and white. The edges are dark red or brown-black. The surface often has pathogenic bacteria and black spots. Spore disk. The leaf sheath became infected. The diseased part showed red small spots and then expanded. Multiple lesions formed irregular plaques. The center was yellow and the edges were red. The diseased part had small black spot-shaped conidia discs.
2 the incidence of disease: red rot is a fungal disease. The growth temperature of the bacteria is 10~37°C, the optimum temperature is 27~35°C, and the PH value is 5~6. If the soil is too acidic and the humidity is high, the disease is serious. The soil is dry and the sugarcane sprouts slowly, which is conducive to the invasion of the bacteria. When the storm is heavy, the mechanical damage rate is high, or the pests are serious and the population of insects is large, the disease is serious. Disease-resistant varieties and rapidly germinating varieties have a mild onset. The pathogenic bacteria in the sugarcane plant, field susceptible plants, diseased stems and soil overwintering became the source of infection in the following year. The spores of the disease spread by means of air, rain, insects and other media. After germination, the pathogens invade the midrib and cane stem tissues through the wound.
(2) Control methods
1 Select disease-resistant seedlings without seedlings and tip cane stalks for seeding.
2 For the first time, the old incision ends are removed first, and then split into two buds, soaked for 1 minute with 50% carbendazim or 50% Benzol WP 400-500 dilution, germination after soaking .
3 to promote the cultivation of plastic film cover, promote early germination, Qimiao fast. Strengthen field management and timely prevention and control of insects and rats.
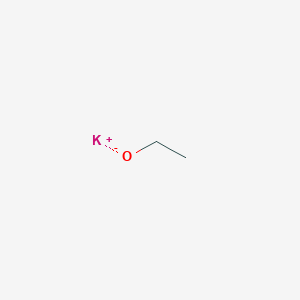
Potassium Ethoxide CAS No.917-58-8
Potassium Ethylate Basic Information
CAS: 917-58-8
MF: C2H5KO
MW: 84.16
EINECS: 213-029-0
Mol File: 917-58-8.mol
Potassium Ethylate Chemical Properties
Melting point 250°C (dec.)
Boiling point -78.5°C (rough estimate)
density 0.894 g/mL at 25 °C
refractive index n20/D 1.39
storage temp. Flammables area
solubility Soluble in ethanol, ether
form Powder
color white to off-white
Water Solubility It reacts vigorously with water.
Sensitive Moisture Sensitive
Stability: Stable, but highly flammable. Reacts violently with water. Contact with damp air may lead to heating of the solid, which could in turn ignite it, or materials with which it is in contact. Incompatible with air, water, moisture, acids, acid chlorides, acid anhydrides, oxidizing agents, reducing agents.
potassium ethoxide,potassium ethoxide in ethanol,potassium methoxide solubility,potassium methoxide boiling point,potassium methoxide in methanol,potassium methoxide msds
ShanDong YingLang Chemical Co.,LTD , https://www.sdylhgtrade.com