Eucalyptus common pest control measures
First, powdery mildew: This disease occurs in nursery seedlings. The temperature is high, humidity is high, seedlings are dense. Poor ventilation conditions are most likely to occur. Gray-brown spots appeared near the main veins on the back of the young leaves, spread over the entire leaves, and there was a layer of white powder. There were also white powder on serious shoots and stems.
Control methods:
1. The nursery should always pay attention to environmental sanitation, properly sparse seedlings, or immediately remove or burn a few diseased plants.
2, when the occurrence of the use of Baume 0.3-0.5 degrees of lime sulfur, spray once every 10, three or four times in a row.
Second, black spot eucalyptus seed germination after emergence 1-4 leaves, prone to this disease. From the tip of the shoot to the root, it turns dark brown and dies.
Control methods Disinfect seeds, soil, and coverings when sowing. At the time of onset, the diseased seedlings were first removed and sprayed with 0.5% potassium permanganate or formalin for two or three times to prevent spread.
3. The alfalfa is more than algebraic in one year and has a long period of damage. The one-year-old seedling suffers serious death and causes death. After the afforestation, the upper leaves of the tree canopy are often eaten. In severe cases, the growth of trees is affected.
Control methods: 0.5 kg of yanghuahua or Tripterygium turfgrass powder plus 75-100 kilograms of fresh water can be used to spray the seedlings, or 90% of trichlorfon or 50% of the marathon emulsion can be sprayed at 2000 times.
4. The leaf roller moth, which occurs several generations a year, feeds shoots on larvae, which affects the high growth of eucalyptus and results in dry bending.
Control methods:
After the new shoots of eucalyptus were removed in January and March, the first-generation larvae were sprayed with 90% trichlorfon, 50% dibromophosphorous emulsion, and 50% marathon emulsion 10,000 times, once every 5 days, two or three times in a row. Can kill larvae. If the larvae have invaded a new shoot, spray 40% dimethoate emulsion 200-300 times.
2, nursery or small area of ​​forest, can be collected in the winter litter burned to eliminate overwintering.
5. Fruit pods generally harm eucalyptus seedlings and saplings under 20 years of age. Two generations occur in one year. The first generation of larvae was endangered from the end of May to the middle of July. The second generation of larvae was damaged in August-September. The larvae clustered on the shoots to feed on leaf shoots, and the silkworms reeled the leaves into bulbous shape, banded the terminal buds, and even the new shoots died, even the whole plant died.
Control methods:
1, when the larvae have not yet formed a net nest, 90% trichlorfon 4000-50000 times jet, you can kill.
2, if the larvae have formed a net nest, it is best to plant it and burn it.
Sixth, Hao Tianniu
1. Adult spawning period (from early May to early June) Brush spawning, spawning or newly hatched larvae with lead wire.
2, artificially cut off the damaged branches, after the injection of dichlorvos and other agents from the drain hole, the larvae will be killed.
Ventilator block diagram
One. Main mechanical ventilation modes
(1) Intermittent Positive Pressure Ventilation (IPPV): positive pressure in the inspiratory phase and zero pressure in the expiratory phase. 1. Working principle: The ventilator generates positive pressure in the inspiratory phase and presses the gas into the lungs. After the pressure rises to a certain level or the inhaled volume reaches a certain level, the ventilator stops supplying air, the exhalation valve opens, and the patient's thorax Passive collapse of the lungs and exhalation. 2. Clinical application: Various patients with respiratory failure mainly based on ventilation function, such as COPD.
(2) Intermittent positive and negative pressure ventilation (IPNPV): the inspiratory phase is positive pressure and the expiratory phase is negative pressure. 1. How it works: The ventilator works both in the inspiratory and exhaled phases. 2. Clinical application: Expiratory negative pressure can cause alveolar collapse and cause iatrogenic atelectasis.
(3) Continuous positive pressure airway ventilation (CPAP): Refers to the patient's spontaneous breathing and artificial positive airway pressure during the entire respiratory cycle. 1. Working principle: Inspiratory phase gives continuous positive pressure air flow, and exhalation phase also gives a certain resistance, so that the airway pressure of inhalation and exhalation phases are higher than atmospheric pressure. 2. Advantages: The continuous positive pressure airflow during inhalation is greater than the inspiratory airflow, which saves the patient's inhalation effort, increases FRC, and prevents the collapse of the airway and alveoli. Can be used for exercise before going offline. 3. Disadvantages: great interference to circulation, large pressure injury of lung tissue.
(4) Intermittent command ventilation and synchronized intermittent command ventilation (IMV / SIMV) IMV: There is no synchronization device, the ventilator air supply does not require the patient's spontaneous breathing trigger, and the time of each air supply in the breathing cycle is not constant. 2. SIMV: There is a synchronization device. The ventilator gives the patient a commanded breath according to the pre-designed breathing parameters every minute. The patient can breathe spontaneously without being affected by the ventilator. 3. Advantages: It exerts its ability to regulate breathing while offline; it has less influence on circulation and lungs than IPPV; it reduces the use of shock medicine to a certain extent. 4. Application: It is generally considered to be used when off-line. When R <5 times / min, it still maintains a good oxygenation state. You can consider off-line. Generally, PSV is added to avoid respiratory muscle fatigue.
(5) Mandatory ventilation per minute (MMV) When spontaneous breathing> preset minute ventilation, the ventilator does not command ventilation, but only provides a continuous positive pressure. 2. When spontaneous breathing is less than the preset minute ventilation volume, the ventilator performs command ventilation to increase the minute ventilation volume to reach the preset level.
(6) Pressure Support Ventilation (PSV) Definition: Under the prerequisite of spontaneous breathing, each inhalation receives a certain level of pressure support, increasing the patient's inhalation depth and inhalation volume. 2. How it works: The inspiratory pressure begins with the patient's inspiratory action, and ends when the inspiratory flow rate decreases to a certain level or the patient attempts to exhale hard. Compared with IPPV, the pressure it supports is constant, and it is adjusted by the feedback of the inspiratory flow rate. Compared with SIMV, it can get pressure support for each inhalation, but the level of support can be set according to different needs. 3. Application: SIMV + PSV: used for preparation before off-line, can reduce breathing work and oxygen consumption Indications: Exercise the ventilator; prepare before going offline; the ventilator is weak due to various reasons; severe flail chest causes abnormal breathing. 5. Note: Generally not used alone, it will produce insufficient or excessive ventilation.
(7) Volume Supported Ventilation (VSV): Each breath is triggered by the patient's spontaneous breathing. The patient can also breathe without any support and can reach the expected TV and MV levels. The ventilator will allow the patient to be truly autonomous Breathing also applies to preparations before going offline.
(8) Capacity control of pressure regulation
(IX) Biphasic or bilevel positive pressure ventilation How it works: P1 is equivalent to inspiratory pressure, P2 is equivalent to breathing pressure, T1 is equivalent to inspiratory time, and T2 is equivalent to exhalation time. 2. Clinical application: (1) When P1 = inspiratory pressure, T1 = inspiratory time, P2 = 0 or PEEP, T2 = expiratory time, which is equivalent to IPPV. (2) When P1 = PEEP, T1 = infinity, P2 = 0, T2 = O, which is equivalent to CPAP. (3) When P1 = inspiratory pressure, T1 = inspiratory time, P2-0 or PEEP, T2 = desired controlled inhalation cycle, equivalent to SIMV.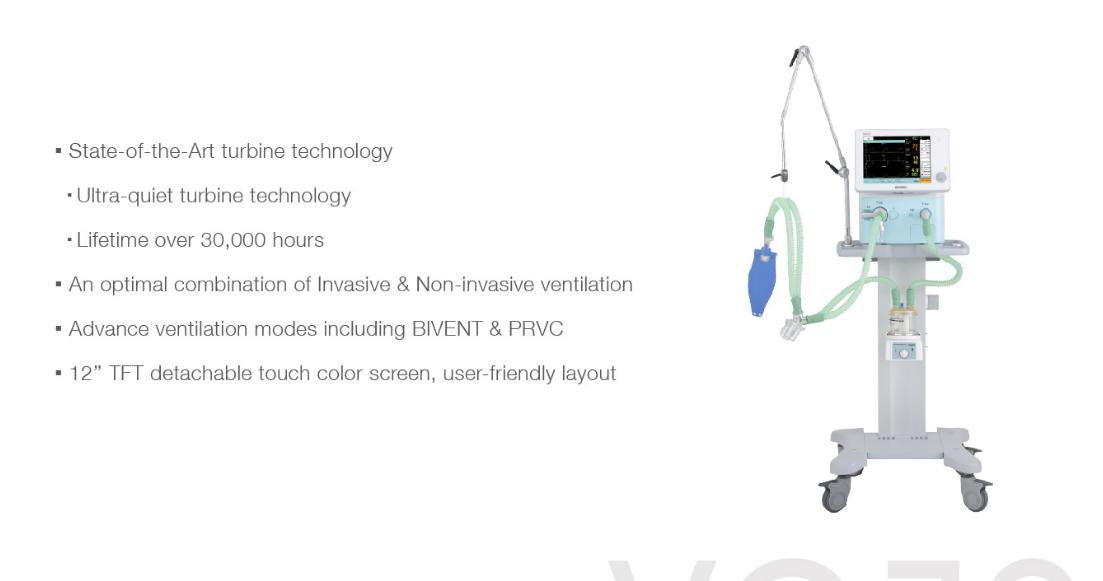
Medical Invasive Breathing Machine
Invasive Breathing Machine,Medical Invasive Ventilator,Invasive Mechanical Ventilation,Invasive Positive Pressure Ventilation
Guangzhou Zhongzhinan Supply Chain Co.,Ltd. , https://www.gzzhongzhinan.com